- Home/
- Role of Diet In Monitoring And Managing Diabetes
Role of Diet In Monitoring And Managing Diabetes

Managing your blood sugar levels is key to living well with diabetes, and consuming the right diet is key to managing your blood sugar levels. Diabetes doesn't mean you cannot eat, it simply means to eat right!
Of all the things that make blood sugar levels rise, food has the biggest rolet to play. Some foods can raise your blood sugar levels more than others and portion size too plays a significant role. What's more, diabetes is different for everyone including the way various foods affect blood glucose. Another reason why diet is so important is because it's one thing you have control over.

Diet plays an important role in managing diabetes
Photo Credit: OneTouch
Dr Kavita Gupta, Director and Nutritionist at Sunil's Diabetes Research and Care Centre, says “choose foods which are low in glycemic Index. The glycemic index ranks carbohydrates on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how quickly they will raise the blood glucose levels after consuming that food. High glycemic index, foods like white bread, rice, potatoes are rapidly digested and can fluctuate blood sugars while foods with a low glycemic index, like whole oats, lentils, soybean are digested slowly & there is a gradual rise in blood glucose levels”.
“High GI foods are rated between 100-70; Medium GI foods are rated between 56-69 and Low GI Foods are rated below 55. Eating high GI foods can cause spikes in blood glucose levels & can lead to an increased risk for type 2 diabetes, heart disease, obesity & may offer anti-inflammatory benefits. People with Diabetes should consume food with a low glycemic index and low glycemic load”, she emphasises.

Some food with their glycemic indices
Photo Credit: OneTouch
Making The Right Food Choices
Unlike a one-size-fits all diet, diabetic diets are highly individualised and must be planned keeping in mind the main principle, which is to support a healthy weight and target blood sugar levels. A diabetic must include all food categories required for healthy living. Here are some general food modifications diabetics should make and make the right food choices:
- Eat more whole grains
- Include brown rice instead of white polished rice
- Switch to multigrain flours like ragi, bajra, jowar, wheat
- Consume more fruits and vegetables
- Choose fresh over frozen, canned fruits
- Eat more dark green and yellow vegetables like cabbage, peas etc
- Choose monounsaturated fats like olive, canola, and peanut oil instead of oils like corn, sesame, safflower
- Avoid trans fats found in bakery products
- Avoid sugary drinks, have vegetable juice or unsweetened fresh fruit juice over sweet fruit juices
- Have tea coffee without sugar or stick to green tea
- Eat nuts in moderation like almonds and walnuts
- Include dried beans and lentils as sources of proteins
- If you are non-vegetarian include fish 2-3 times a week and choose skinless chicken
- Choose low-fat dairy products to reduce fat and cholesterol content
People with diabetes should know the carbohydrate content in various foods to make the right choices. Carbs are the starches and sugar content in food that raise the blood sugar levels faster than other foods. Indian diets tend to be carb-rich hence sugar levels tend to be higher post meals. Discuss with your dietician or diabetes educator the right amount of carbs for you to keep a track of the amount eaten and set a limit.
According to Dr Kavita, “India is carbo-rich country where the emphasis is more on simple carbs and sweets, fat and processed bakery items. These should be replaced with more complex carbs and more fibre. Including the right amount of protein, fibre & fat also blunts the spike in the blood glucose levels. For example, consuming an egg or a moong dal cheela with paneer or an omelette, legumes or a bowl of salad shall blunt the post prandial spike.”
How Testing Your Blood Sugar Around Meals Helps?
Your blood sugar level changes throughout the day. It's affected by food, activity, and medication. Testing your blood sugar levels with the glucometer before and after your meals helps you see the immediate effect of your food choices and portions on your blood sugars, which can then help take the right steps to manage high or low blood sugar levels. Dr Kavita adds, “the quantity and quality of meals affects your blood glucose values hence a self monitoring of blood (SMBG) chart is important to ascertain and act as per the values”.

Importance of testing blood sugar at meals
Photo Credit: OneTouch
Testing your blood glucose both before and after a meal helps you analyse how meals affect your blood glucose levels and helps you to understand which meals may be best for optimal blood glucose control. Pre and post meal testing allows you to see how your meal, and also medication, affects your blood sugar values. A chart helps to discuss your regime with your doctor or consultant to re-evaluate your diet or meal choices.
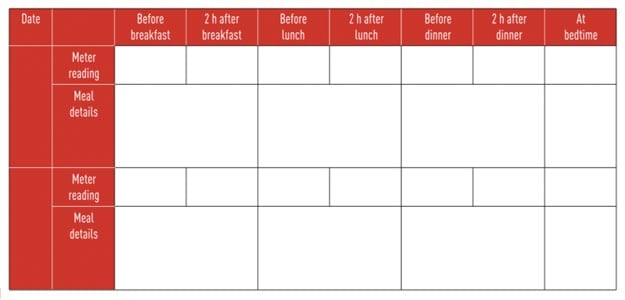
Make a chart like this to tabulate your blood sugar values
Photo Credit: OneTouch
Use Test Results To Keep Blood Sugars In Range
Keeping your blood sugar levels in a healthy range can not only help prevent serious diabetes complications, it can also help you feel better and empowered to manage your diabetes better. Test your blood sugar before and after a meal to see if your food intake is helping to keep your values within target range. Maintaining a blood glucose chart is extremely important as it helps to know whether or not and when the values are going high or low. These values can then be used to check with your doctor or diabetes educator as to what you should do about it.
For example, if your post-meal test result is more than 50 mg/dl higher than your before-meal result, next time try eating a smaller portion of carbohydrates. Always follow your healthcare professional's recommendations for testing. Test both before and after a meal to see if your food and portion sizes are working to keep your sugar levels under control.
Blood sugar monitoring around meals also helps to keep a check on incidence of low blood sugar levels or hypoglycaemia, which is a serious condition and can be life threatening. If you feel any symptoms of low blood glucose like tingling lips, sweating, anxious, dizziness etc., check your sugars and if they are less than 70 mg/dl, take 15 g of carbs or 3 teaspoons of sugar and recheck values after 15 minutes. In case the sugar levels have not risen repeat the steps.
A healthy diet is hence the pillar of a successful diabetes management plan. Other pillars include regular exercise, managing stress, and taking any medications as prescribed. To summarise, Dr Kavita Gupta explains the ABCDE of Diabetes:
A is the A1C test, which should be less than 7%
B for blood Pressure 130/80 mg/dl
C is for bad cholesterol levels (LDL) which should be less than 100
D for Diet
E Exercise Regularly
also read
Videos
Show MoreFood Items That Can Help Prevent Diabetes
Managing Diabetes - A Touch Away

According to the 9th edition of the Diabetes Atlas by the International Diabetes Foundation, 1 in 6 people with Diabetes in the world are from India.
With an estimated 77 million people with Diabetes, India is number two in the world after China (116 million) in terms of the most number of diabetics in the world.
Given the epidemic proportions and the spread of the disease, it is important to know not just about prevention measures but also how a diabetic can effectively manage the disease.
The NDTV campaign, Managing Diabetes - A Touch Away, supported by One Touch aims to highlight the importance of regular and meaningful monitoring of blood glucose at home in addition to lifestyle changes and medication in managing Diabetes