- Home/
- One Lakh Excess Premature Deaths Linked To Air Pollution In 8 Indian Cities
One Lakh Excess Premature Deaths Linked To Air Pollution In 8 Indian Cities
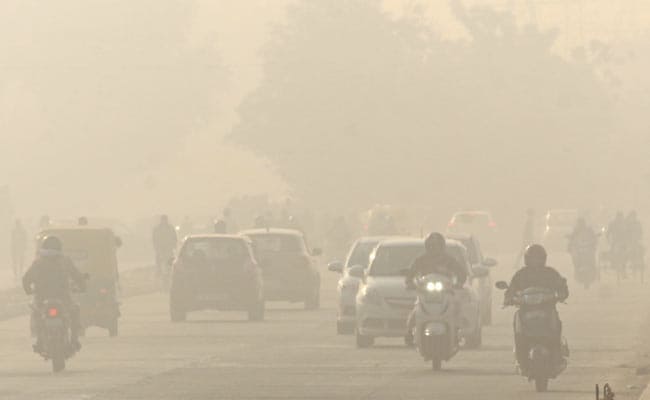

Exposure to air pollution has been linked to 100,000 excess premature deaths in the Indian cities of Mumbai, Bangalore, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Chennai, Surat, Pune and Ahmedabad between 2005 and 2018, according to a study.
The international team of scientists aimed to address data gaps in air quality for 46 cities in Africa, Asia and the Middle East using space-based observations from instruments onboard NASA and European Space Agency (ESA) satellites for 2005 to 2018.
The study, published last week in the journal Science Advances, shows rapid degradation in air quality and increases in urban exposure to air pollutants which are hazardous to health.
The researchers found significant annual increases in pollutants directly hazardous to health of up to 14 per cent for nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and up to 8 per cent for fine particles (PM2.5).
They also found increase in the level of up to 12 per cent for ammonia and up to 11 per cent for reactive volatile organic compounds.
The team, including researchers from the Harvard University in the US, attributed this rapid degradation in air quality to emerging industries and residential sources like road traffic, waste burning, and widespread use of charcoal and fuelwood.
"Open burning of biomass for land clearance and agricultural waste disposal has in the past overwhelmingly dominated air pollution in the tropics," said study lead author Karn Vohra from University College London (UCL) in the UK.
"Our analysis suggests we are entering a new era of air pollution in these cities, with some experiencing rates of degradation in a year that other cities experience in a decade," said Vohra, who completed the study as a Ph.D. student at the University of Birmingham, UK.
The researchers also found 1.5 to four-fold increases in urban population exposure to air pollution in 40 of the 46 cities for NO2 and 33 of the 46 cities for PM2.5, caused by a combination of population growth and rapid deterioration in air quality.
The study found that the increase in the number of people dying prematurely from exposure to air pollution was highest in cities in South Asia.
Dhaka, Bangladesh, saw a total of 24,000 excess premature deaths, while the Indian cities of Mumbai, Bangalore, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Chennai, Surat, Pune and Ahmedabad had 100,000 excess deaths.
The researchers noted that India has an extensive network of monitors operated and maintained by local and national authorities as well as research institutions.
However, the use of these for informing policies is hindered by data quality issues for the national network and restricted access to data collected by research institutions and state governments, they said.
The number of deaths in tropical cities in Africa are currently lower due to recent improvements in healthcare across the continent resulting in a decline in overall premature mortality, the researchers said.
However, the worst effects of air pollution on health will likely occur in the coming decades, they said.
"We continue to shift air pollution from one region to the next, rather than learning from errors of the past and ensuring rapid industrialisation and economic development don't harm public health," said study co-author Eloise Marais from UCL.
"We hope our results will incentivise preventative action in the tropics," Marais added.
also read
Man Reveals How The Car He 'Regretted' Buying Saved His Daughter's Lungs
Edited by Abhinav SinghWatch: Delhi Woman Living In Bengaluru Says She Wants To Move Parents Out Of "This Gas Chamber"
Edited by Srishti Singh SisodiaVideos Show "Dangerous" Situation In Delhi NCR As It Chokes Under Dense Smog
Edited by Srishti Singh Sisodia
Latest Stories
- Edited by Abhinav Singh | Tuesday December 16, 2025
A father shared how his Maruti Fronx protected his daughter's lungs from pollution during a trip between Panvel and Nashik.
- Edited by Srishti Singh Sisodia | Monday December 15, 2025
Delhi's air quality has been a major concern, with the city's Air Quality Index (AQI) worsening to the 'severe plus' category.
- Written by Toshita Sahni | Monday December 15, 2025
A UK traveller's video about running into a visibility problem when visiting the famous Taj Mahal in Agra has resonated with many. The post is also viral at a time when North India is facing serious air pollution concerns.
- Edited by Srishti Singh Sisodia | Monday December 15, 2025
The severe air quality poses significant health risks, particularly for children and the elderly.
- Reported by Ankita Tiwari | Monday December 15, 2025 , New Delhi
A thick toxic haze blanketed Delhi today morning, reducing visibility and disrupting flights and train schedules as the capital battled hazardous air quality.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Latest Videos
Opinion
Blog | Well Done, Delhi. You've Turned Lung Sacrifice Into A Badge Of HonourSaikat Kumar Bose
Monday November 10, 2025Till some years back, Delhiites would ask angry questions to those in power about the capitals annual tryst with toxic air. This has changed. Those in the driving seat dont see the need to answer now.
Opinion | Why Indians Have Just Given Up On Air Pollution CrisisTanushree Ganguly
Friday December 20, 2024While some may argue that people in Delhi are now more aware of air pollution than they were a decade back, my rebuttal would be that awareness does not mean that people are concerned.
Opinion | You Must Outrage Over Filthy Air More Than Once A YearJyoti Pande Lavakare
Tuesday December 10, 2024Delhi welcomed us with monsoon rains and mangos. We were home. Fast forward a couple of years, in the winter of 2012, I found myself in denial about something other parents, mostly expats, were calling toxic air.
Opinion | Delhi's Air Pollution Situation Is Like A Bad MarriageNishtha Gautam
Friday November 22, 2024On a good day, such as today, the AQI reading in Delhi is 407. We are jubilant at the sickly sunshine trickling through the slightly dissipated smog. At least its not 1600.
दिवाली... पराली... सियासी जुगाली!Ashwini kumar
Monday November 18, 2024दिल्ली-एनसीआर में प्रदूषण का समाधान तो आज तक मिला नहीं. हर साल चिंतित होकर हम-आप सांसों की तकलीफ के साथ-साथ दिल और ब्लड प्रेशर के मरीज भी क्यों बनें?