- Home/
- Plastic Pollution Threatens Human Health: Study
Plastic Pollution Threatens Human Health: Study

Highlights
- Plastic pollution poses a significant, under-recognised threat to human and planetary health
- Microplastics have been found in human tissues, warranting a precautionary approach
- Open burning of plastic waste contributes majorly to air pollution in low- and middle-income countries
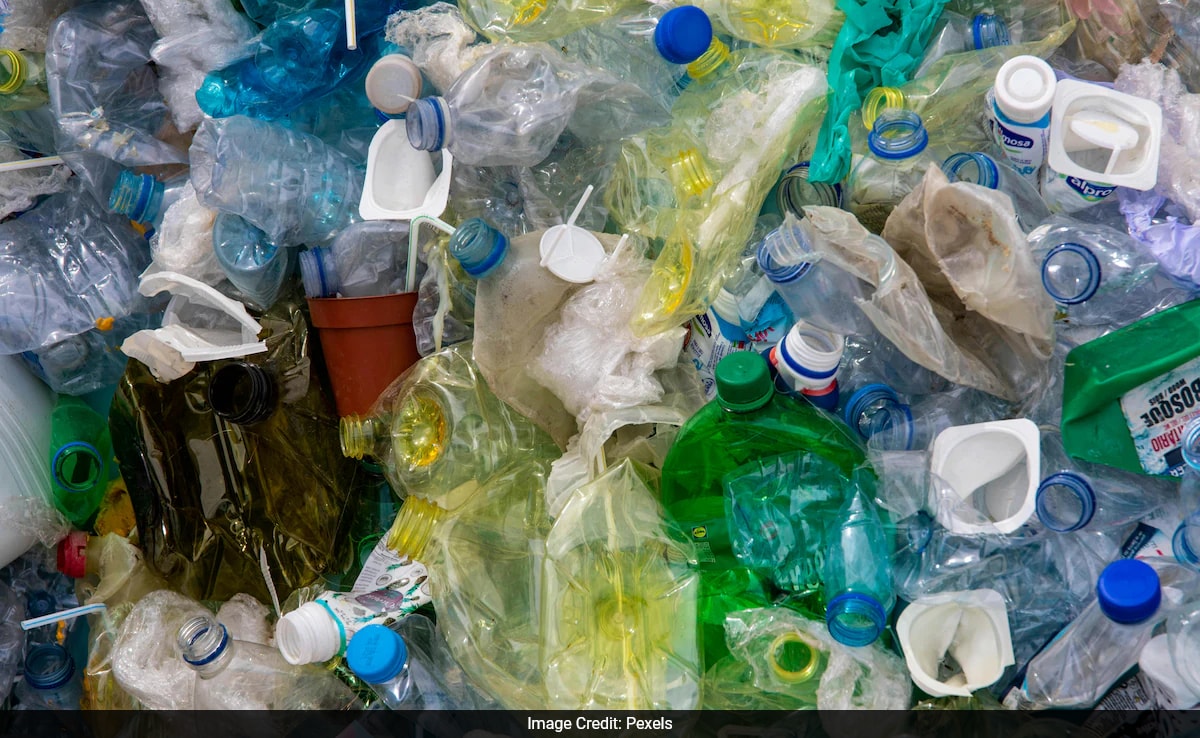
Ahead of the UN treaty on plastics, a new report in The Lancet journal on Monday has warned that plastic pollution is an underrecognised threat to the health of both humans and the planet, which must be addressed immediately.
The report, led by a group of international experts, reviews the current evidence on how plastics -- including microplastics and plastic chemicals -- impact health.
"Plastics are a grave, growing, and under-recognised danger to human and planetary health. Plastics cause disease and death from infancy to old age and are responsible for health-related economic losses exceeding $1.5 trillion annually," said corresponding author Prof Philip J Landrigan, from Boston College, US.
The report discusses evidence that plastics endanger human health at every stage of their life cycle -- in production, use, and disposal. It showed that airborne emissions from plastic production include particulate matter (PM2.5), sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides, as well as hazardous chemicals to which plastic workers can be exposed.
The experts from the US, Switzerland, Germany, and Australia noted the lack of transparency around which chemicals are present in plastics, their production volumes, uses, and known or potential toxicity.
"Many plastic chemicals are associated with multiple health effects at all stages of human life," the experts said.
Further, the report stated that microplastics have been reported in human tissues and body fluids, and, while further research is needed to understand the relationship with potential health impacts, a precautionary approach is warranted.
An estimated 57 per cent of unmanaged plastic waste is burned in the open -- a major source of air pollution in low-and middle-income countries.
Plastic waste can also provide a habitat for mosquitoes to lay their eggs and for the growth of microorganisms, potentially contributing to the spread of vector-borne diseases and antimicrobial resistance, said the experts.
They called for a greater focus on health impacts when considering plastic pollution.
Notably, the report projected that, without changes, plastic production will almost triple between 2019 and 2060.
Landrigan stated that while "continued worsening of plastics' harms is not inevitable," it can be mitigated cost-effectively by evidence-based, transparently tracked, effectively implemented, and adequately financed laws and policies.
To address plastics' harms globally, UN member states unanimously resolved in 2022 to develop a comprehensive, legally binding instrument on plastic pollution, namely the Global Plastics Treaty, covering the full lifecycle of plastic. The meeting is scheduled for tomorrow.
Meanwhile, the experts also announced the launch of a new project to track the impact of plastics: the Lancet Countdown on Health and Plastics.
"The Lancet Countdown on Health and Plastics will identify and track a series of indicators that document the impacts of plastics and plastic chemicals on human health across all stages of the plastic life cycle. The first indicator report is expected in mid-2026," Landrigan said.
(Except for the headline, this story has not been edited by NDTV staff and is published from a syndicated feed.)
also read
Mumbai Pollution Linked To 57% Of Lung Cancer Cases: Maharashtra Government Warns of Health Crisis
Written by Shreya GoswamiInside Bengal's 800-Km "Green Wall" Along Jharkhand Border To Fight Air Pollution
Reported by Rittick MondalUnited Nations Approves First Carbon Credits Under Paris Agreement
Agence France-Presse
Latest Stories
- Written by Shreya Goswami | Friday February 27, 2026
Rising air pollution in Mumbai is now being linked to 57% of lung cancer cases, the Maharashtra government told the state assembly.
- Reported by Rittick Mondal | Thursday February 26, 2026 , Kolkata
The Mamata Banerjee-led government plans to set up an 800-km long greeen corridor, which will work as a "bioshield" - a forested area that would act as a "Green Wall" - along the Jharkhand border to intercept pollutants entering Bengal.
- Agence France-Presse | Thursday February 26, 2026 , Paris
The United Nations announced the approval of the first carbon credits under a global market aimed at reducing emissions, a mechanism that has faced scrutiny over greenwashing concerns.
- Wednesday February 25, 2026 , New Delhi
Air pollution is a concern not just for Mumbai but for countries and cities around the world, Maharashtra Environment Minister Pankaja Munde told NDTV Wednesday, after the city woke this morning to a blanket of smog for an eighth straight day.
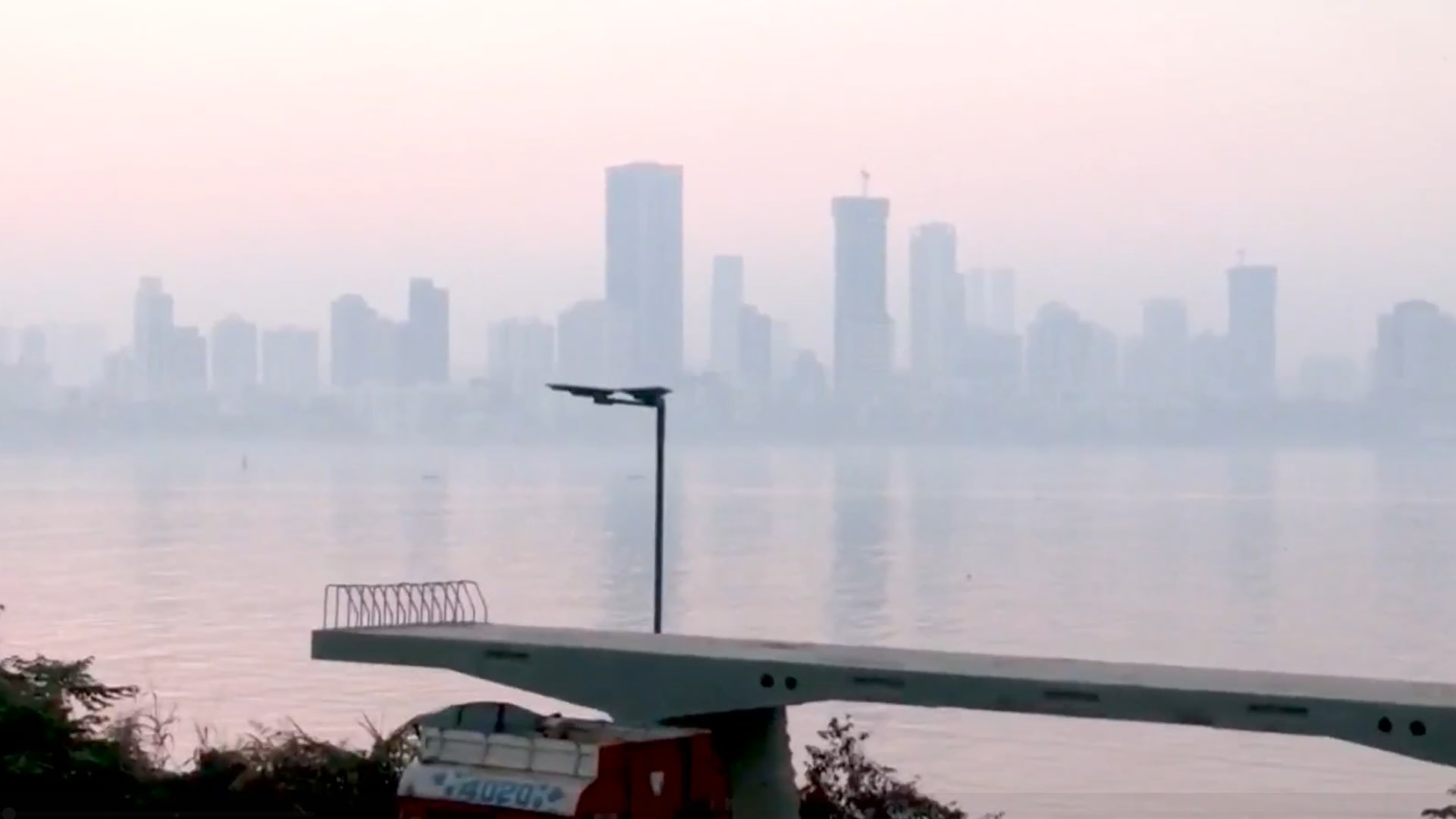
- Reported by Radhika Ramaswamy | Thursday February 26, 2026 , Mumbai
Mumbai woke up to yet another blanket of haze on Tuesday morning, with a grey veil hanging over the skyline from Bandra to South Mumbai.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Latest Videos
Opinion
Blog | Well Done, Delhi. You've Turned Lung Sacrifice Into A Badge Of HonourSaikat Kumar Bose
Monday November 10, 2025Till some years back, Delhiites would ask angry questions to those in power about the capitals annual tryst with toxic air. This has changed. Those in the driving seat dont see the need to answer now.
Opinion | Why Indians Have Just Given Up On Air Pollution CrisisTanushree Ganguly
Friday December 20, 2024While some may argue that people in Delhi are now more aware of air pollution than they were a decade back, my rebuttal would be that awareness does not mean that people are concerned.
Opinion | You Must Outrage Over Filthy Air More Than Once A YearJyoti Pande Lavakare
Tuesday December 10, 2024Delhi welcomed us with monsoon rains and mangos. We were home. Fast forward a couple of years, in the winter of 2012, I found myself in denial about something other parents, mostly expats, were calling toxic air.
Opinion | Delhi's Air Pollution Situation Is Like A Bad MarriageNishtha Gautam
Friday November 22, 2024On a good day, such as today, the AQI reading in Delhi is 407. We are jubilant at the sickly sunshine trickling through the slightly dissipated smog. At least its not 1600.
दिवाली... पराली... सियासी जुगाली!Ashwini kumar
Monday November 18, 2024दिल्ली-एनसीआर में प्रदूषण का समाधान तो आज तक मिला नहीं. हर साल चिंतित होकर हम-आप सांसों की तकलीफ के साथ-साथ दिल और ब्लड प्रेशर के मरीज भी क्यों बनें?